Diagnostic methods for breast cancer used in India
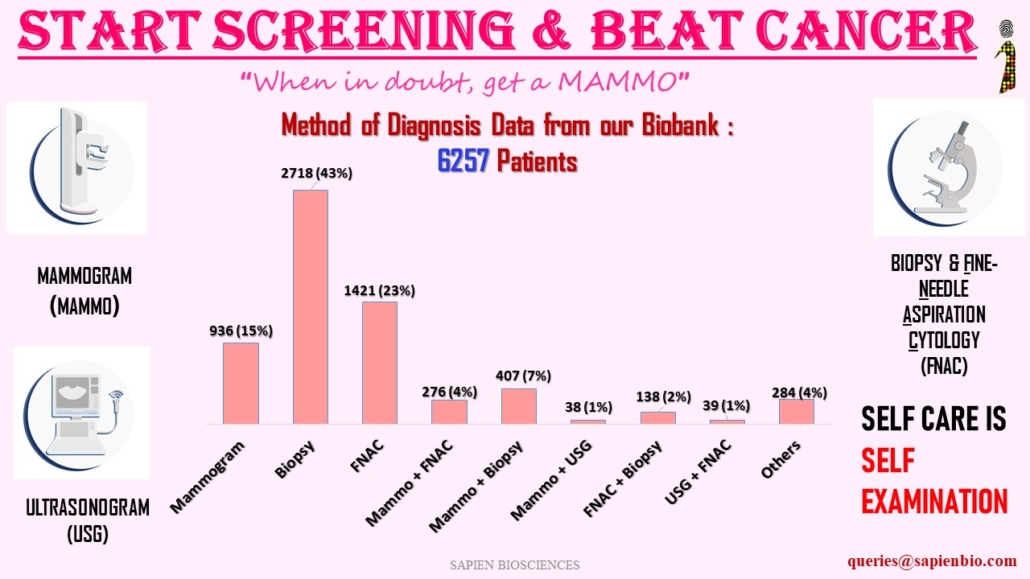
Breast cancer can be diagnosed through multiple tests, including a mammogram, self-examination, ultrasound, MRI and biopsy. If the doctor finds an area of concern on a screening test (a mammogram), or if the patient has symptoms that could mean breast cancer, then more tests need to be done in order to diagnose whether it is cancer or not. The most common symptom of breast cancer is a new lump or mass. Breast cancer is sometimes found after symptoms appear, but many women with breast cancer have no symptoms. This is why regular breast cancer screening is so important. Any change in breast should be checked by a physician.
Most widely used methods of diagnosis are as follows:
1) Mammograms : low-dose x-rays
2) Ultrasound (USG) : sound waves and their echoes to make computer pictures of the inside of the breast. It can show certain breast changes, like fluid-filled cysts, that can be harder to see on mammograms.
3) MRI : radio waves and strong magnets to make detailed pictures of the inside of the breast.
4) Biopsy including Core needle biopsy, FNAC, or Surgical biopsy: this is done when mammograms, or another imaging test, or a physical exam shows a breast change that may be cancer.
A biopsy is the only way to know for sure if it’s cancer.
References:
Breast Cancer Mode of Detection in a Population-Based Cohort- 2022-
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36737116
Tru-Cut Biopsy versus Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Diagnosis of Early Breast Cancer-2023 https://ijmpr.in/article/Tru-Cut+Biopsy+versus+Fine+Needle+Aspiration+Cytology+in+Diagnosis+of+Early+Breast+Cancer
Fine-needle aspiration cytology versus core needle lymph node biopsy in axillary staging of breast cancer – 2022 https://ejrnm.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s43055-022-00895-w
Comparison of ultrasound and mammography for early diagnosis of breast cancer among Chinese women with suspected breast lesions: A prospective trial – 2022
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9663682/

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!